Advanced Security Certbot
Advanced Security Certbot
- In class Certbot questions activity
- Hacks
- To install and setup Certbot follow these instructions:
- Unsecured HTTP connection
- Secure HTTPS connection
- You are most likely done with your hacks if you have reached this point.
Certbot is a software run in Python. It is meant to convert HTTP sites to work with HTTPS, which is much more secure. Let’s first explore the background of HTTP to HTTPS: HTTPS and HTTP are almost essentially the same protocols, but HTTPS uses SSL to encrypt the requests and responses. Furthermore, HTTPS is also used in the form of SSL certificates used to encrypt and digitally sign these requests. HTTP runs on port 80, and is an incredibly insecure platform to run a site on. HTTPS runs on ports 80 and 443, and needs a Certification Authority signature for the SSL certificate being used on the https site. APPLICATION IN CSP, PROS/CONS During Trimester 1, while initially setting up our AWS deployment, we attempted to implement Let’s Encrypt, a certificate authority manager, along with Certbot. The Certbot configuration is relatively easy: as shown in Trimester 1, you have to install a couple of packages, create the certbot folders on the AWS deployment server, and activate HTTPS for your domain.
Though it is relatively easy to use, we decided to weigh out some of the pros/cons of using Let’s Encrypt & Certbot: PROS:
- Let’s Encrypt is a free service.
- It is issued very efficiently.
- It is something that most of our students are already familiar with, so it is a smoother process to setup. CONS:
- Certificates have to be replaced/renewed every 90 days. This can be a painful process, especially for multiple sites and groups to do.
- Some domains block Let’s Encrypt, and have relationships with other SSL providers.
- It is a platform that is vulnerable to malware attacks. Almost 15 thousand Let’s Encrypt certificates have been issued to phishing sites. Is this another risk that we want to factor in? In our opinion, this can still be a useful tool, because it means that some Let’s Encrypt sites are dangerous, while millions of others are much safer. It is still important to keep in mind.
- Most private domains that you use Certbot to secure cost money to purchase and use.
In class Certbot questions activity
- What service owns Certbot?
- How often do certificates need to be replaced/renewed?
- How many certificates have been issued by Certbot?
Hacks
- Follow the instructions below and provide a full screenshot of all terminal commands after and including
sudo certbot --apacheall the way until it asks for the domain you want to secure. At this point you can take a screenshot and cancel the process. If you choose to continue the setup process and get Certbot fully working and show a before and after screenshot of your domain with http amd https connection we will grant extra credit points on hacks, or make up for lost points in other areas.

To install and setup Certbot follow these instructions:
- You will first need to have a domain that is not yet secured. You can check if it is secure by going to the domain on your browser and making sure that there is no lock symbol at the top, or that the prefix to the domain is http, rather than https. Be careful here because some of you may have your domain already secured, and I am not sure what would happen if you did this on an already secure domain. Getting a domain will cost around 7$ a year so I cannot demonstrate this step, nor expect anyone else to. Lots of people would already have their AWS running with Certbot, so if you don’t have a domain to use don’t worry as that last step won’t be necessary.
Unsecured HTTP connection
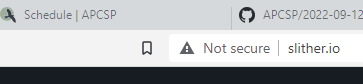
Secure HTTPS connection
-
Install Certbot through the terminal with the following command
sudo apt-get install certbot -
Next we have to choose a plugin to obtain and install the certificates. For Apache web servers, you can use the following command. If you are using a different browser engine, you can choose the corresponding plugin for that browser engine. You might have issues with this if you don’t have the apache plugin installed. To fix this run the command
sudo apt-get install python3-certbot-apache. After that run the second line of code.sudo certbot --apache -
Next, you will need to follow the given prompts and Certbot will help us set the rest up. You will need to enter your email for renewals and other things. It will also ask to share your email with another organization, to which you can respond no.
You are most likely done with your hacks if you have reached this point.
-
You will have to create a DNS text record with a specific value that certbot can use to make sure you actually have ownership of the domain.
-
Now you have to verify the installation and you can check if it’s working by checking the website in your browser, or using a tool such as SSL Labs, which can check for an SSL certificate.
-
This is optional. Now you can ensure that your certbot will continue working with minimum maintenance. You can do this by making the certificate auto renew using this command.
sudo certbot renew